-40%
Julius Caesar AR Denarius 40 BC Rome Mint -Very Rare Variety-
$ 700.92
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
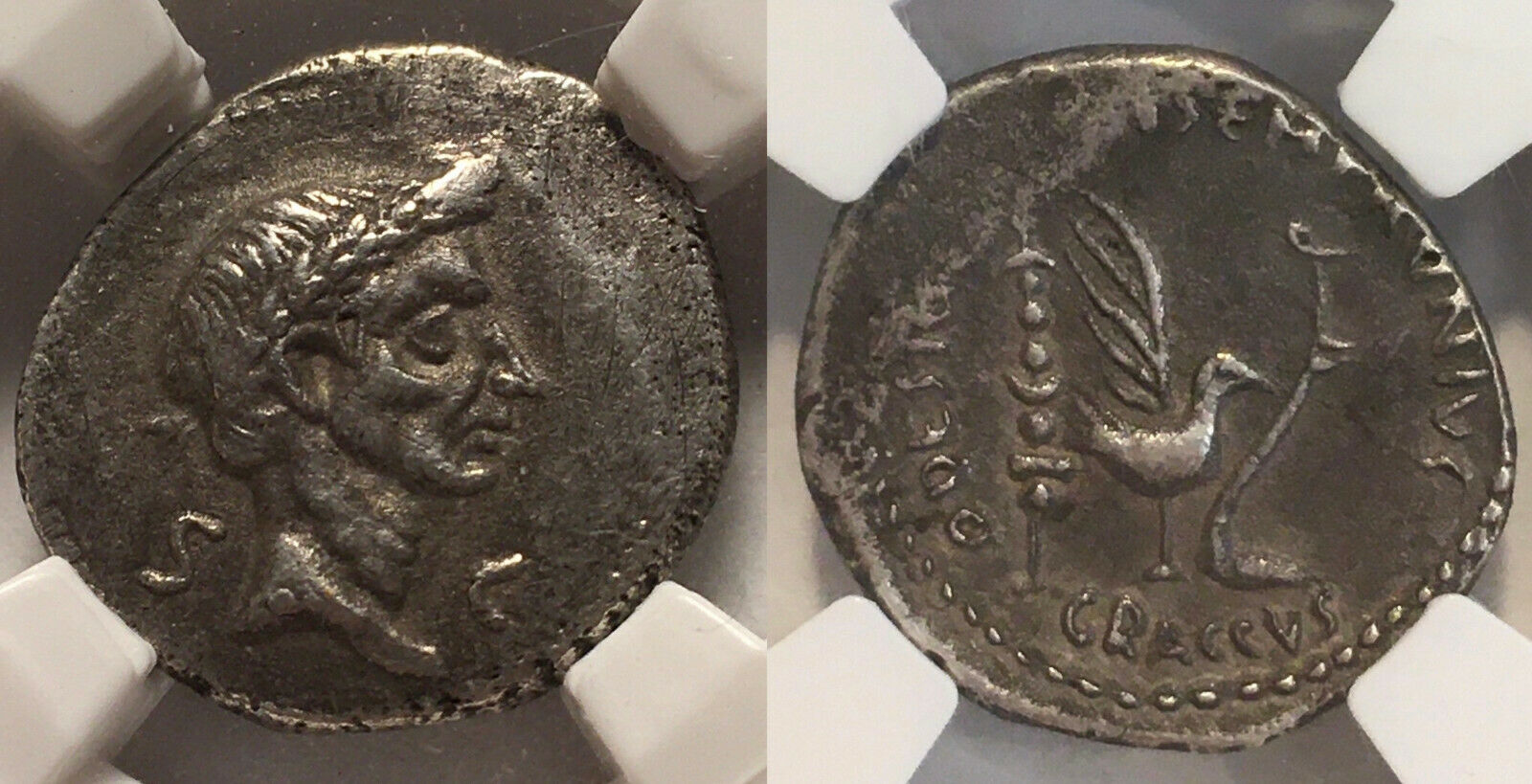
Julius Caesar AR Denarius 40 BC Rome Mint -Very Rare Variety-The Caesarians.
Julius Caesar.
40 BC. AR Denarius (18mm, 3.79 g, 9h). Rome mint; Ti. Sempronius Gracchus,
quaestor designatus
. Wreathed head right; S C flanking neck / Signum, aquila, plow, and
decempeda
(measuring rod); TI • SEMPRONIVS above; GRACCVS in exergue; • Q • DESIG to left. Crawford 525/4a; CRI 327a; Sydenham 1129; RSC 47; Kestner 3636; BMCRR Rome 4319; RBW 1811; CNR 11/5. VF, toned,
Ancient test mark/punch mark on obverse near temple of the bust.
Very rare.
History of Julius Caesar:
Gaius Julius Caesar
(Latin:
[ˈɡaːiʊs ˈjuːliʊs ˈkae̯sar]
; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC) was a
Roman
general and statesman. A member of the
First Triumvirate
, Caesar led the Roman armies in the
Gallic Wars
before defeating
Pompey
in a civil war
and governing the
Roman Republic
as a dictator from 49 BC until
his assassination
in 44 BC.
In 60 BC, Caesar,
Crassus
and
Pompey
formed the
First Triumvirate
, a political alliance that dominated
Roman politics
for several years. Their attempts to amass power as
Populares
were opposed by the
Optimates
within the
Roman Senate
, among them
Cato the Younger
with the frequent support of
Cicero
. Caesar rose to become one of the most powerful politicians in the Roman Republic through a string of military victories in the
Gallic Wars
, completed by 51 BC, which greatly extended Roman territory. During this time he both
invaded Britain
and
built a bridge across the Rhine river
. These achievements and the support of his veteran army threatened to eclipse the standing of Pompey, who had realigned himself with the Senate after the
death of Crassus
in 53 BC. With the Gallic Wars concluded, the Senate ordered Caesar to step down from his military command and return to Rome. Leaving his command in Gaul would mean losing his immunity to criminal prosecution by his enemies; knowing this, Caesar openly defied the Senate's authority by
crossing the Rubicon
and marching towards Rome at the head of an army.
This began
Caesar's civil war
, which he won, leaving him in a position of near unchallenged power and influence.
After assuming control of government, Caesar began a program of social and governmental reforms, including the creation of the
Julian calendar
. He gave citizenship to many residents of far regions of the Roman Republic. He initiated land reform and support for veterans. He centralized the bureaucracy of the Republic and was eventually proclaimed "dictator for life" (
dictator perpetuo
). His populist and authoritarian reforms angered the elites, who began to conspire against him. On the
Ides of March
(15 March), 44 BC,
Caesar was assassinated
by a group of rebellious senators led by
Brutus
and
Cassius
, who stabbed him to death.
A new
series of civil wars
broke out and the
constitutional government of the Republic
was never fully restored. Caesar's great-nephew and adopted heir Octavian, later known as
Augustus
, rose to sole power after defeating his opponents in the
last civil war of the Roman Republic
. Octavian set about solidifying his power, and the era of the
Roman Empire
began.
Caesar was an accomplished author and historian as well as a statesman; much of his life is known from his own accounts of his military campaigns. Other contemporary sources include the letters and speeches of Cicero and the historical writings of
Sallust
. Later biographies of Caesar by
Suetonius
and
Plutarch
are also important sources. Caesar is considered by many historians to be one of the greatest military commanders in history.
His
cognomen
was subsequently adopted as a
synonym
for "
Emperor
"; the title "
Caesar
" was used throughout the Roman Empire, giving rise to modern
cognates
such as
Kaiser
and
Tsar
. He has
frequently appeared in literary and artistic works
, and his political philosophy, known as
Caesarism
, inspired politicians into the modern era.